| Name: | BISABOLOL |
|---|---|
| CAS:: | 23089-26-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C15H26O |
| Standard: | Cosmetic grade |
| Development stage: | Commercialization |
| Production Process: | Biological fermentation |
Related Products
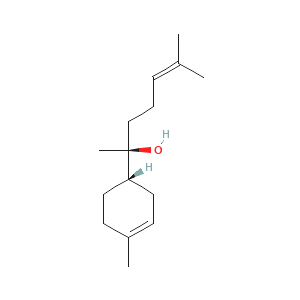
BISABOLOL
Bisabolol, or more formally α-(−)-bisabolol or also known as levomenol,is a natural monocyclic sesquiterpene alcohol. It is a colorless viscous oil that is the primary constituent of the essential oil from German chamomile (Matricaria recutita) and Myoporum crassifolium. High concentrations of bisabolol can also be found in certain medicinal cannabis cultivars. It is poorly soluble in water and glycerine, but soluble in ethanol. The enantiomer, α-(+)-bisabolol, is also found naturally but is rare. Synthetic bisabolol is usually a racemic mixture of the two, α-(±)-bisabolol. It is the terpenoid responsible for distinctive aroma of chamomile flowers, and when isolated, its scent has also has been likened to apples, sugar and honey.
Bisabolol has a weak sweet floral aroma and is used in various fragrances. It has also been used for hundreds of years in cosmetics because of its skin healing properties including reducing wrinkles, skin toughness and repairing sun-damaged skin, and more recently it has been compounded with tretinoin as a topical treatment for acne. Bisabolol is known to have anti-irritant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-microbial properties.Bisabolol is also demonstrated to enhance the percutaneous absorption of certain molecules and has found use as a penetration enhancer: an agent used in topical formulations, increasing the substances propensity for absorption beneath the skin.